Introduction
Sometimes, a baby is born with a food pipe that does not connect properly to the stomach. This condition is known as Esophageal atresia. It is a medical emergency that needs immediate attention. The newborn finds it difficult to swallow milk and may choke or cough during feeding. Understanding esophageal atresia meaning and its treatment options helps parents stay calm and make informed decisions for the baby’s health.
Doctors use advanced surgical techniques and neonatal care to manage the condition. With early esophageal atresia treatment, most babies recover well and grow normally. This blog explains everything – esophageal atresia types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment in a clear and user-friendly way.
What Is Esophageal Atresia?
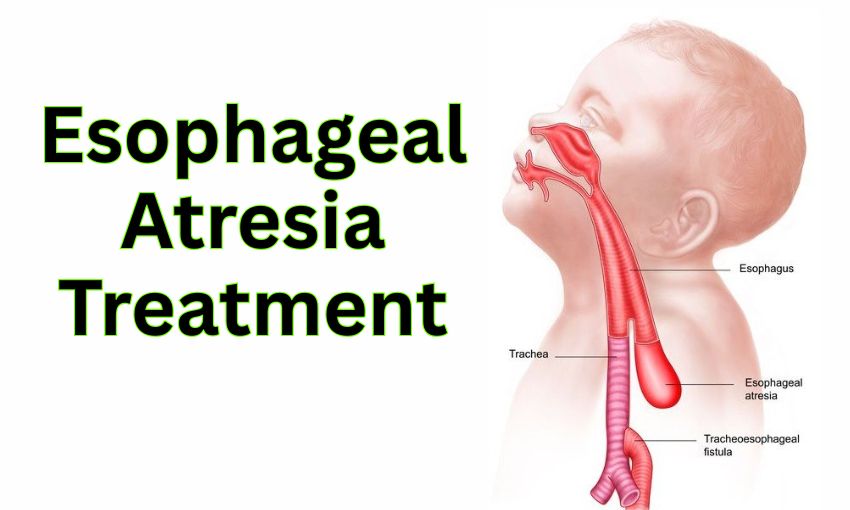
Esophageal atresia meaning refers to a birth defect where the esophagus (food pipe) is not properly connected to the stomach. Due to this condition, babies cannot swallow milk. Sometimes, a connection forms between the trachea (windpipe) and esophagus, which is known as tracheoesophageal fistula. Both conditions are serious and require surgery.
Esophageal Atresia Types
Doctors identify different esophageal atresia types depending on how the esophagus is formed:
| Type | Description |
| Type A | Upper esophagus and lower esophagus end separately and do not connect. |
| Type B | Upper part connects to the trachea, lower part ends blindly. |
| Type C | Most common type – lower esophagus connects to trachea. |
| Type D | Rare and complex – both ends connect to the trachea. |
Type C accounts for almost 85% of cases and often occurs with tracheoesophageal fistula.
Esophageal Atresia Causes
The exact esophageal atresia causes are still not fully known. However, doctors believe genetics and environmental factors may play a role during pregnancy. Some possible causes include:
- Genetic mutations during fetal development
- Maternal diabetes
- Certain medications during pregnancy
- Poor fetal growth
- Abnormal development of the digestive or respiratory system
It rarely occurs due to anything the mother did wrong. Regular prenatal check-ups help in early detection.
Symptoms of Esophageal Atresia
Parents may notice the symptoms right after birth. Common symptoms of esophageal atresia include:
- Difficulty swallowing milk
- Excessive drooling or saliva
- Coughing or choking during feeding
- Bluish skin during feeding (due to lack of oxygen)
- Breathing problems
- Inability to gain weight
Doctors quickly diagnose the problem if feeding is not possible. Immediate hospitalization is necessary.
Diagnosis of Esophageal Atresia
Proper diagnosis helps plan esophageal atresia treatment. Doctors may use the following tests:
- Physical Examination – Checking feeding and breathing patterns
- X-ray with a feeding tube – To see where the esophagus ends
- Ultrasound
- Echocardiogram – To check related heart defects
- Blood Tests – To check infection or other issues
Early detection improves recovery chances.
Esophageal Atresia Treatment – How Doctors Manage It
The only effective esophageal atresia treatment is surgery. Doctors perform corrective surgery soon after birth. The procedure depends on esophageal atresia types and the baby’s overall health.
Steps in Treatment
- Stabilizing the Baby – Doctors prevent choking and infections using a suction tube.
- Surgery – The esophagus is joined to the stomach. If a tracheoesophageal fistula exists, it is closed.
- IV Nutrition – Baby receives nutrition through a vein until feeding becomes safe.
- Post-Surgery Care – Monitoring breathing, digestion, and infections.
- Feeding Therapy – Helps the baby learn safe swallowing.
Most babies recover and grow normally after surgery. Follow-up care is important to prevent complications.
Post-Surgery Care for the Baby
After esophageal atresia treatment, doctors suggest special care:
- Feed only as per doctor’s advice
- Keep the baby upright during feeding
- Use small, frequent meals
- Attend regular follow-up visits
- Watch for vomiting or breathing issues
- Avoid infections and seasonal flu
- Maintain hygiene while preparing milk
A nutritionist may recommend a special diet for proper growth.
Possible Complications
Some babies may develop minor complications after surgery. They can be managed with proper care.
| Complication | Description |
| Acid reflux | Stomach acid comes into the esophagus |
| Narrowing of esophagus | May require dilation procedure |
| Breathing problems | Due to repaired esophagus area |
| Difficulty swallowing | Needs therapy and exercises |
Parents must stay alert and report any problem immediately.
Life After Treatment – Can the Baby Live Normally?
With modern esophageal atresia treatment, most children grow normally and live healthy lives. Regular check-ups, proper feeding support, and monitoring help in recovery. The child may need speech therapy, feeding therapy, or physiotherapy in some cases.
Early surgery and proper care make a big difference. Many adults today live a normal life after successful transesophageal atresia treatment during infancy.
How Parents Can Support Their Child
Parents play a vital role in recovery. Simple steps can make a big difference:
- Stay informed about the condition
- Follow the feeding schedule strictly
- Avoid self-medication
- Keep medical records safe
- Join support groups for guidance
- Provide love and emotional support
A calm and hopeful environment helps the baby recover better.
Conclusion
Esophageal atresia is a rare birth defect, but modern medical science provides effective solutions. Early diagnosis and timely esophageal atresia treatment help the baby recover well. Understanding transesophageal atresia, symptoms, causes, and esophageal atresia types allows parents to take the right steps. With proper post-surgery care, most children grow healthy and lead normal lives. Hope, awareness, and timely action are the keys to successful recovery.
10 FAQs About Esophageal Atresia Treatment
- What is esophageal atresia meaning?
It is a birth defect where the food pipe does not connect properly to the stomach, making swallowing difficult. - What causes esophageal atresia?
The exact cause is not known. It may be linked to genetics, poor fetal development, or maternal health conditions. - What are the symptoms of esophageal atresia?
Symptoms include choking during feeding, drooling, coughing, and breathing trouble. - What is transesophageal atresia?
It is a condition where the esophagus does not connect to the stomach properly and requires surgery. - What is tracheoesophageal fistula?
It is an abnormal connection between the windpipe and food pipe, often seen with esophageal atresia. - How is esophageal atresia treatment done?
Surgery is the only treatment. The esophagus is joined, and any fistula is closed. - Can babies live normally after treatment?
Yes, with timely surgery and care, most babies live a healthy life. - Are there different esophageal atresia types?
Yes, Type A, B, C, and D exist. Type C is the most common. - How soon is surgery done?
Usually within the first few days of birth. - Can feeding be done normally after surgery?
With proper therapy and guidance, babies learn to swallow safely and grow normally.